What are Galvanized Steel, Galvalume Steel, and Zinc Aluminum Magnesium Coated Steel?
When you selecting coated steel for construction, roofing, and other applications, the choices often coil down to Galvanized Steel, Galvalume Steel, and Zinc Aluminum Magnesium (ZAM) Coated Steel. These materials have unique properties that make them suitable for specific environments and purposes. Here’s a detailed look at their characteristics and differences:
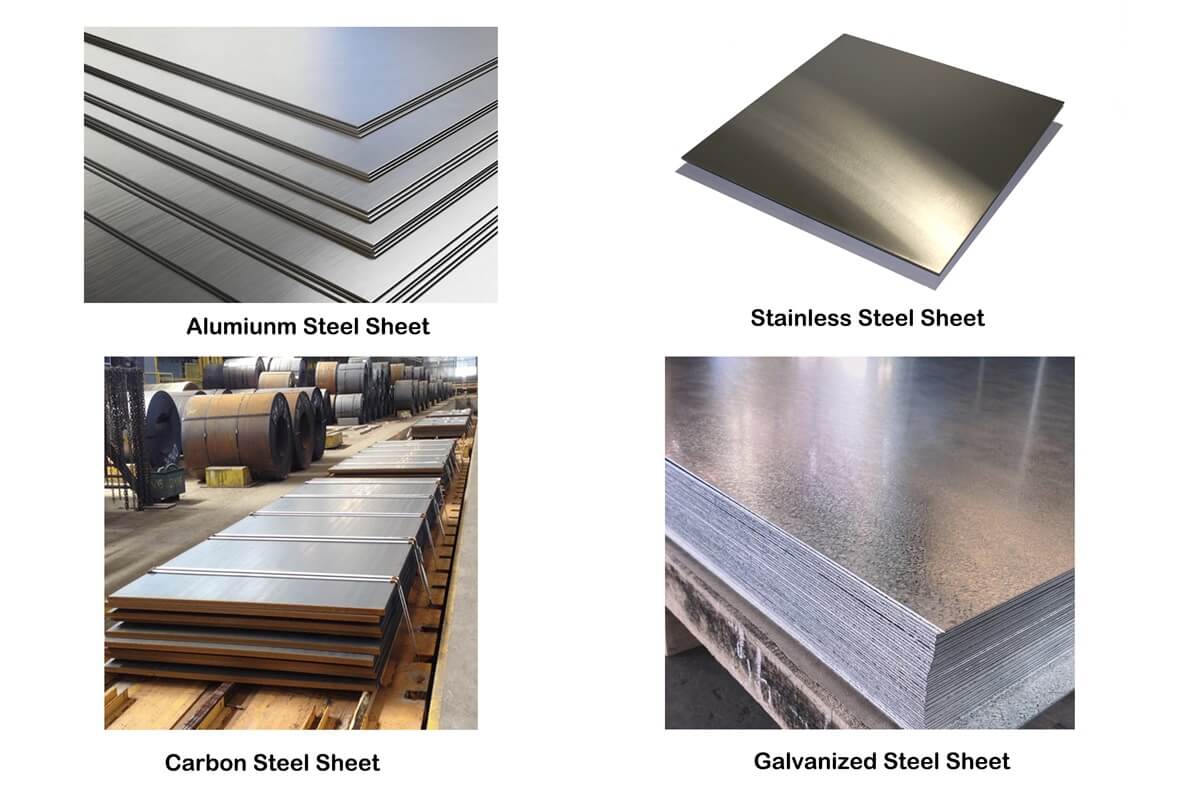
Galvanized Steel
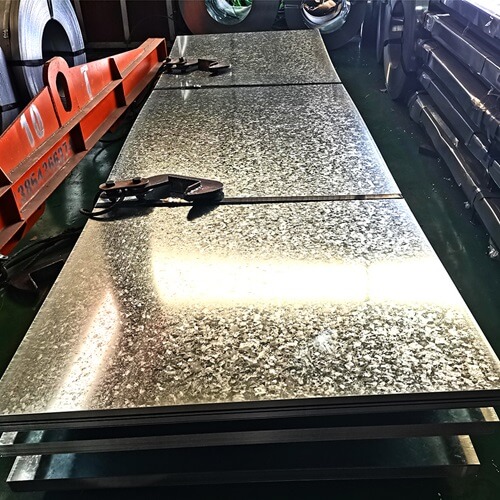
Galvanized Steel is a steel sheet in coil coated with a layer of zinc to protect against rust corrosion. The coating is typically applied through a hot-dip process, where the steel is immersed in molten zinc.
Key Characteristics:
- Corrosion Resistance: Provides good protection against rust and corrosion in typical outdoor environments. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer, which corrodes first before the steel does.
- Durability: Suitable for general construction, roofing, and automotive parts but can be susceptible to rust in highly corrosive environments, such as coastal or industrial areas.
- Surface Appearance: Has a typical spangled or mottled appearance due to the crystallization of zinc.
- Cost: Generally cost-effective compared to other coated steels.
Common Applications:
- Used in roofing, automotive body parts, structural beams, and other construction materials.
Galvalume Steel
Galvalume Steel is similar to galvanized steel but with a coating made of an aluminum-zinc alloy (usually 55% aluminum, 43.4% zinc, and 1.6% silicon). This combination offers enhanced protection compared to traditional galvanized steel.
Key Characteristics:
- Corrosion Resistance: Provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine and industrial environments. The aluminum offers barrier protection while the zinc provides sacrificial protection.
- Durability: Has a longer lifespan than galvanized steel in most environments due to its enhanced resistance to rust and corrosion.
- Heat Resistance: Better resistance to high temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring thermal endurance.
- Surface Finish: Typically has a smooth, shiny finish with a fine spangle pattern.
Common Applications:
- The common usually for roofing, siding, HVAC systems, and other exterior applications where long-term durability is critical.
Zinc Aluminum Magnesium (ZAM) Coated Steel
ZAM Coated Steel is a newer type of coated steel that includes zinc, aluminum, and magnesium in the coating (usually around 90-96% zinc, 1-6% aluminum, and 1-3% magnesium). This combination significantly improves corrosion resistance.
Key Characteristics:
- Corrosion Resistance: Offers the highest level of corrosion protection among the three, particularly in extreme environments like coastal areas with high salt content.
- Self-Healing Properties: The magnesium component allows the coating to self-heal scratches and cut edges, offering protection even if the surface is damaged.
- Surface Finish: Has a smoother and more uniform appearance compared to galvanized and Galvalume steels.
- Durability: Extremely durable with excellent long-term resistance to rust and corrosion.
Common Applications:
- Used in high-end roofing, structural components, and areas exposed to harsh weather or corrosive elements.
Differences Summary
- Coating Composition:
- Galvanized Steel: Zinc coating.
- Galvalume Steel: Aluminum-zinc alloy coating.
- ZAM Coated Steel: Zinc-aluminum-magnesium alloy coating.
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Galvanized Steel: Good in general environments but less effective in highly corrosive areas.
- Galvalume Steel: Better resistance due to the aluminum-zinc mix.
- ZAM Coated Steel: Superior resistance, especially in aggressive environments, thanks to magnesium’s self-healing properties.
- Cost:
- Galvanized Steel: Typically the least expensive.
- Galvalume Steel: Moderately priced, offering good value for its enhanced properties.
- ZAM Coated Steel: Generally more expensive due to its advanced coating and superior performance.
- Applications:
- Galvanized Steel: Suitable for everyday applications where extreme corrosion resistance isn’t required.
- Galvalume Steel: Ideal for environments requiring more robust protection.
- ZAM Coated Steel: Best for challenging environments with high corrosion risks, such as coastal and industrial applications.
Choosing the right type of coated steel depends on the specific requirements of your project, including the environment, budget, and desired lifespan. Galvanized Steel is great for general use, Galvalume Steel offers enhanced durability for moderately corrosive settings, and ZAM Coated Steel is the best choice for maximum protection in harsh conditions.