Introduction
Sheet metal is one of the most versatile and widely used materials across industries. From construction and automotive to HVAC systems and household applications, sheet metal plays a critical role in shaping modern infrastructure and technology. This guide dives into various types of sheet metals, including PPGI steel, aluminum sheet metal 4×8, stainless steel sheet, and more, while exploring manufacturing techniques and applications.
What Is Sheet Metal?
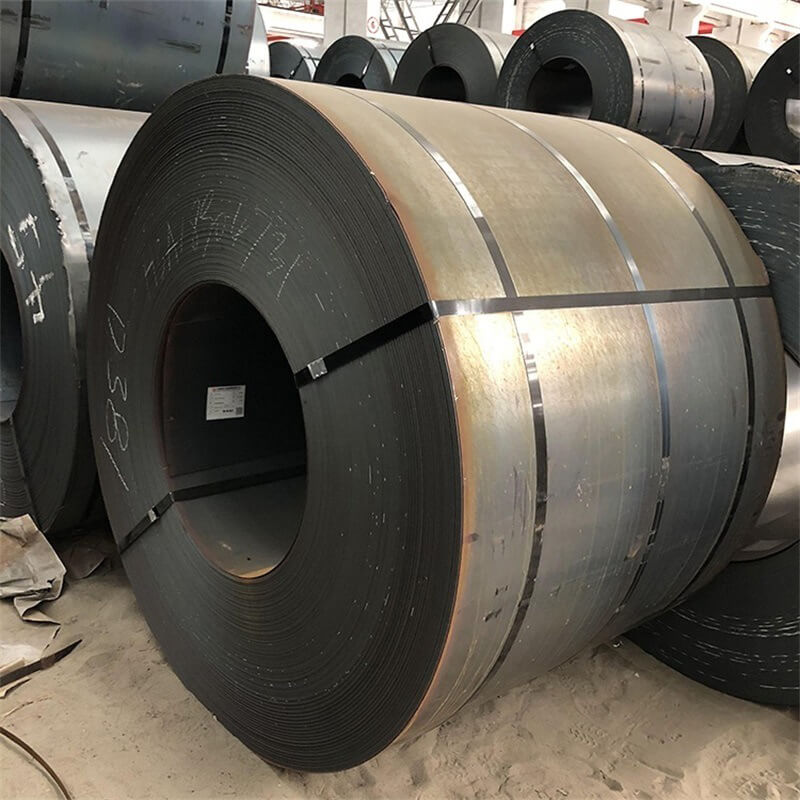
Sheet metal refers to thin, flat pieces of metal formed through an industrial process. These sheets can be cut, bent, and formed into various shapes, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. Common sheet metal materials include aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, and galvanized metals.
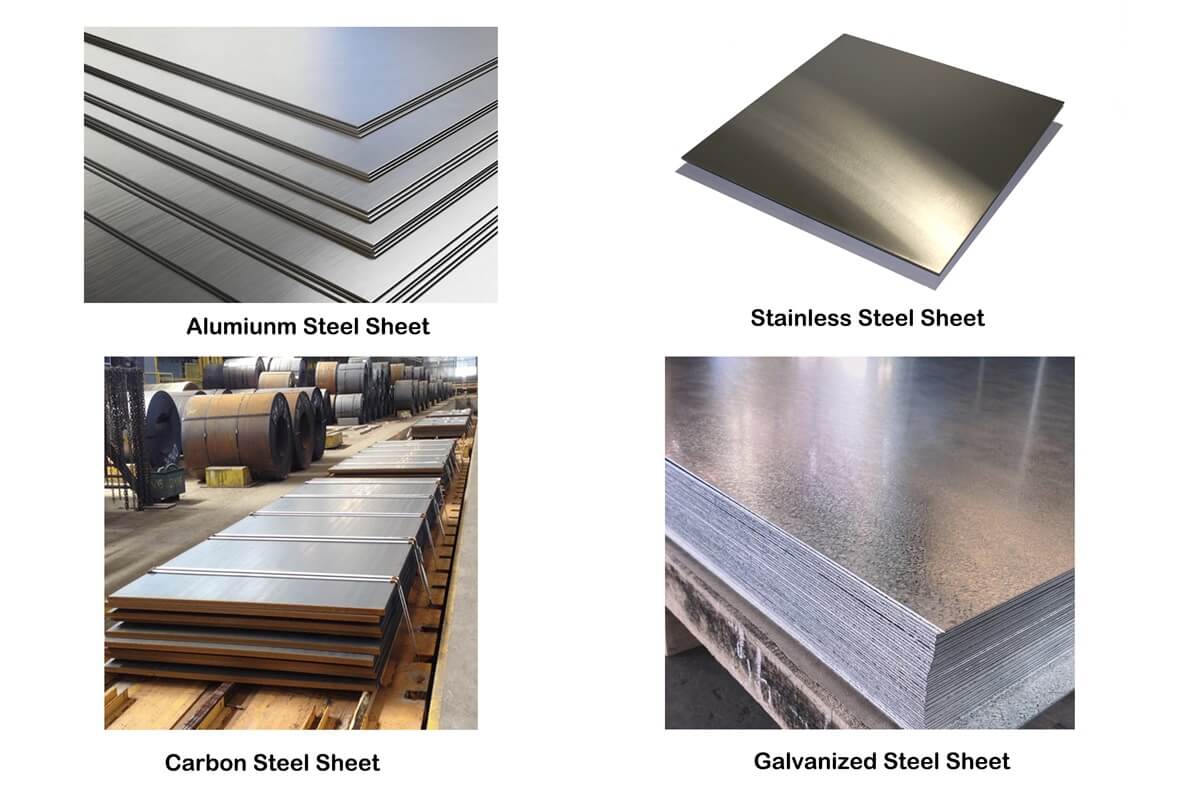

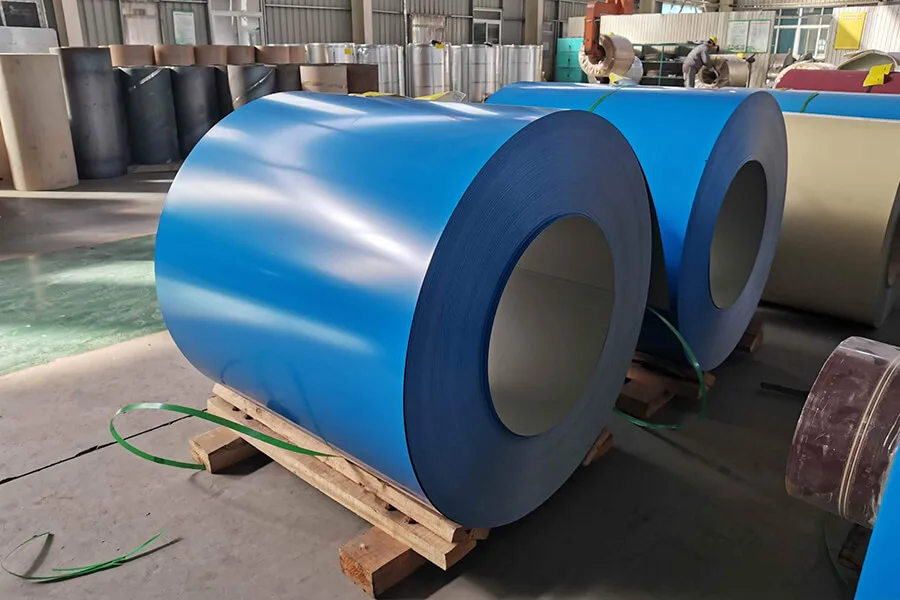
PPGI Steel: Pre-Painted Galvanized Innovation
PPGI steel, or Pre-Painted Galvanized Iron, is steel that has been coated with zinc and painted with protective layers. It’s widely used in roofing, wall panels, and appliances. Its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal make it an attractive option in both residential and industrial applications.
PPGI steel is not just durable; it’s also customizable in color and finish. It is often preferred over bare galvanized steel in visible applications where appearance matters.
Aluminum Sheet Metals: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
One of the most popular types of sheet metal is aluminum sheet metal. Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it a go-to material in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries.
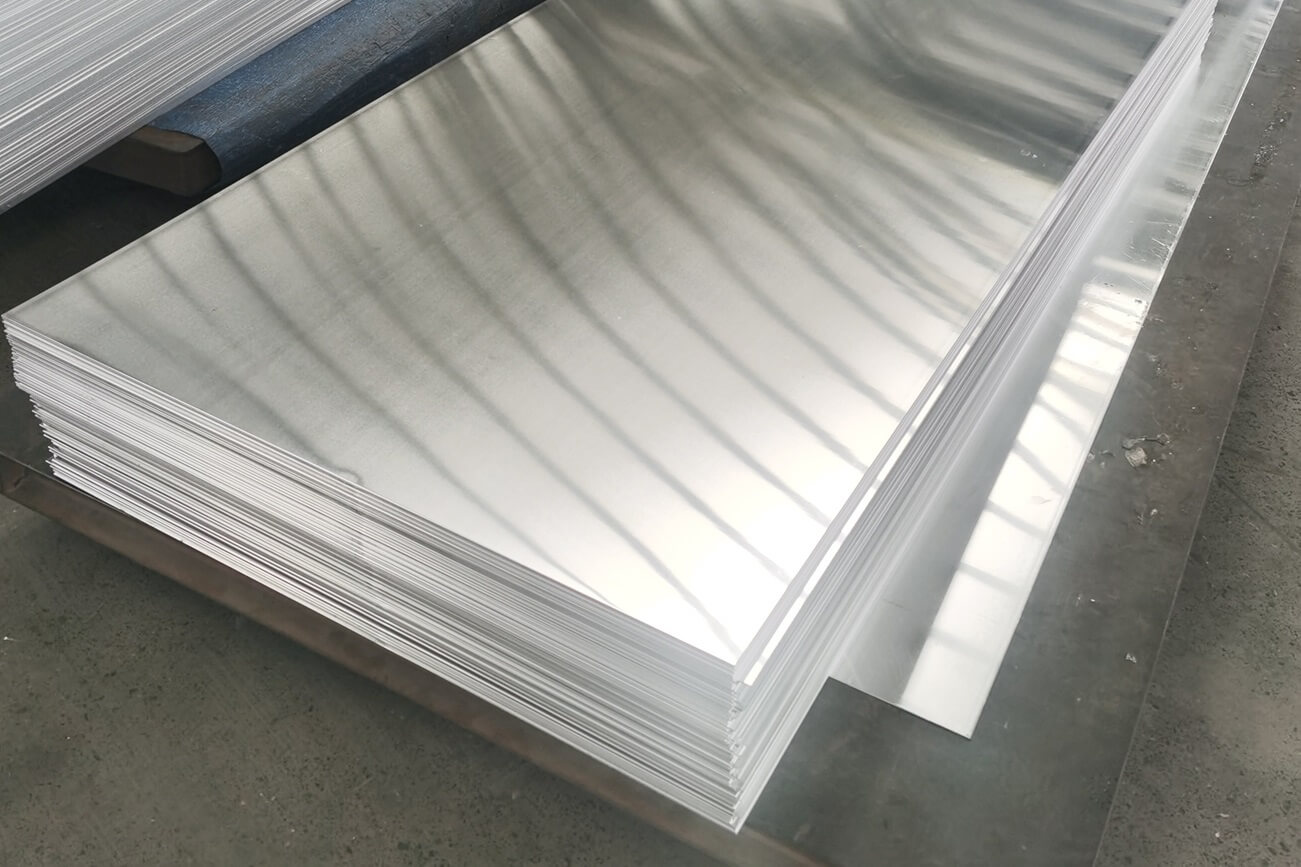
Aluminum Sheet Metals 4×8
The 4×8 aluminum sheet metals is a standard size used across many industries. These dimensions—4 feet by 8 feet—are ideal for fabrication, offering sufficient surface area for construction and design. Whether you’re building HVAC ducts or boat hulls, this size is commonly stocked and easy to work with.
Alu Sheet Metal and Alum Sheet Metal
You might see the terms alu sheet metals or alum sheet metals used interchangeably with aluminum sheet. These shorthand versions are popular in informal or industrial contexts, but they all refer to the same durable and versatile metal.
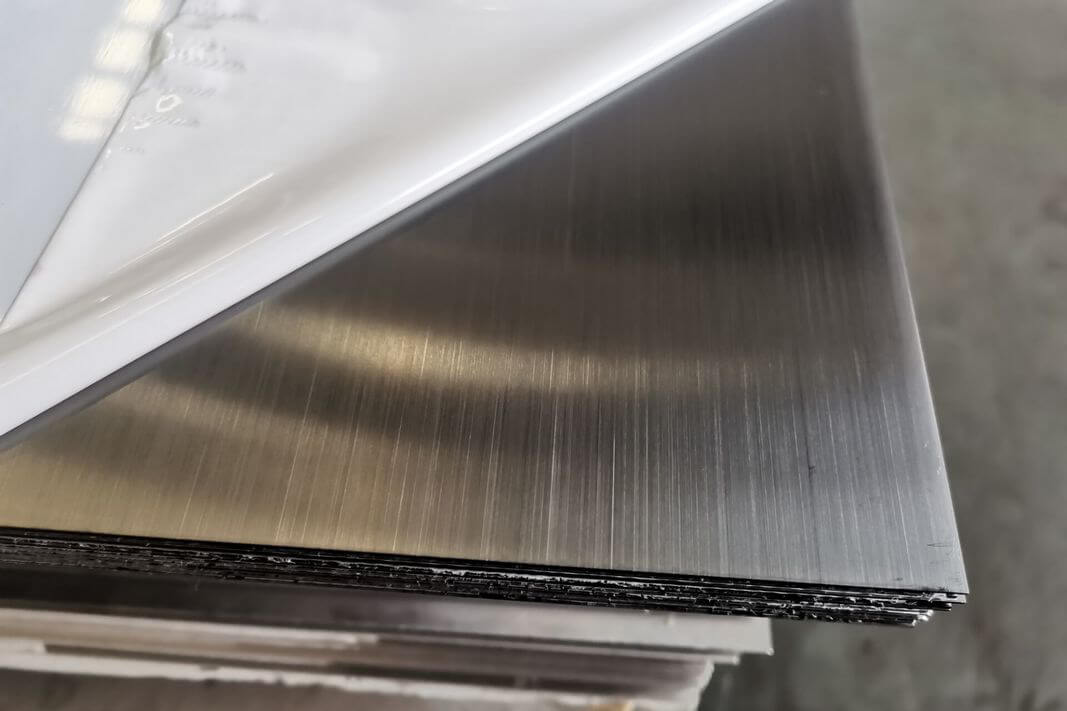
Stainless Steel Sheet: Strength Meets Aesthetics
Stainless steel sheet is renowned for its strength, rust resistance, and sleek appearance. It’s widely used in kitchen equipment, surgical tools, and architectural elements.
Stainless Steel Sheet Metal
Stainless steel sheet metals provides the same corrosion resistance as stainless steel sheets, but is often used in fabrication processes that require cutting, bending, or stamping. It’s perfect for heavy-duty applications where strength and hygiene are critical, like food processing plants or hospitals.
316L Stainless Steel
Among the different grades, 316L stainless steel stands out for its superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine and chemical environments. The “L” in 316L stands for “low carbon,” which enhances weld ability without compromising strength. If you’re working with sheet metal in harsh conditions, this grade is an excellent choice.
Black Sheet Metal: A Stylish Choice
Black sheet metals typically refers to steel that has been treated or coated to achieve a dark finish. It’s a stylish and modern material used in architectural design, furniture, and decorative applications. While it may not offer the same corrosion resistance as galvanized or stainless steel, its aesthetic appeal is unmatched in certain applications.
Flat Sheet Metal: The Basic Form
Flat sheet metals refers to sheets that have not been corrugated, embossed, or otherwise shaped. These sheets are easy to store, transport, and process. Whether it’s aluminum, stainless steel, or PPGI, flat sheets are the foundation of sheet metal manufacturing.
Sheet Metal Roller: A Must-Have Tool
To shape flat sheets into curves or cylinders, a sheet metal roller is essential. This tool allows fabricators to create round ducts, tanks, and other cylindrical forms. Rollers come in manual and powered versions, suitable for both small workshops and industrial operations.
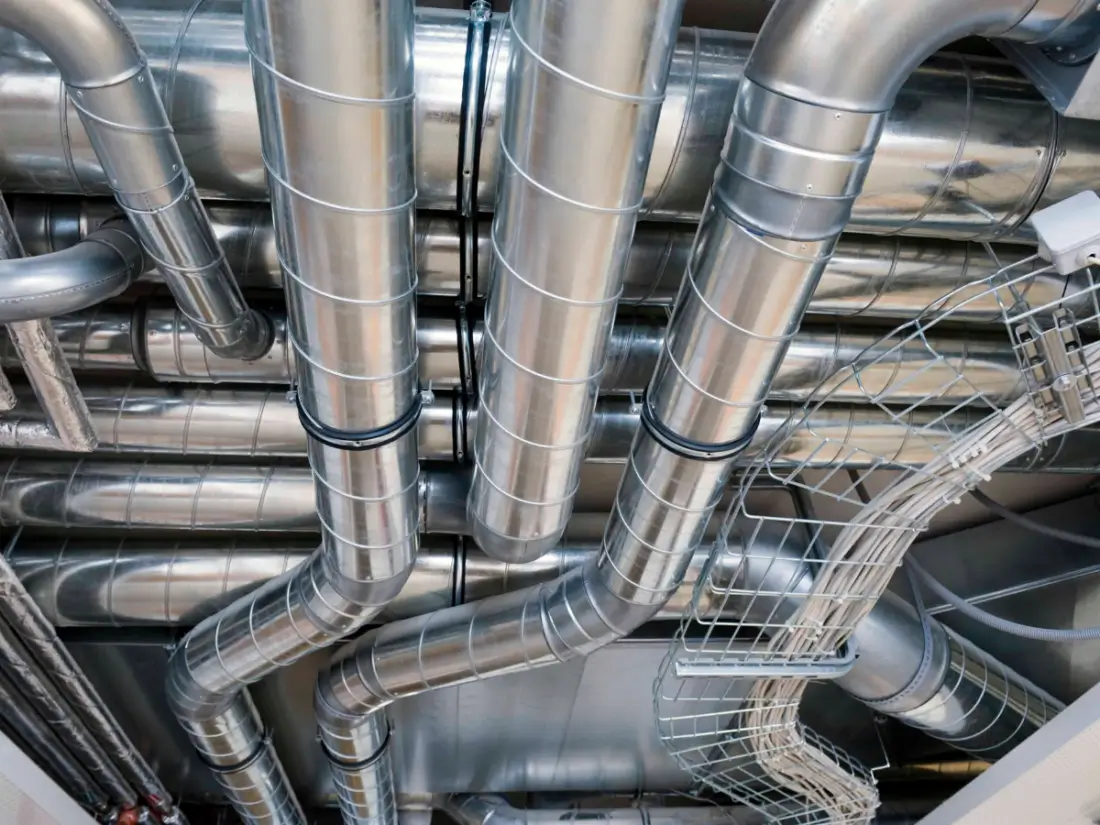
HVAC Sheet Metals: Keeping Things Cool (or Hot)
In the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning industry, HVAC sheet metals is used to fabricate ducts, vents, and enclosures. Typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum, these sheets are chosen for their ability to withstand air pressure, humidity, and temperature fluctuations.
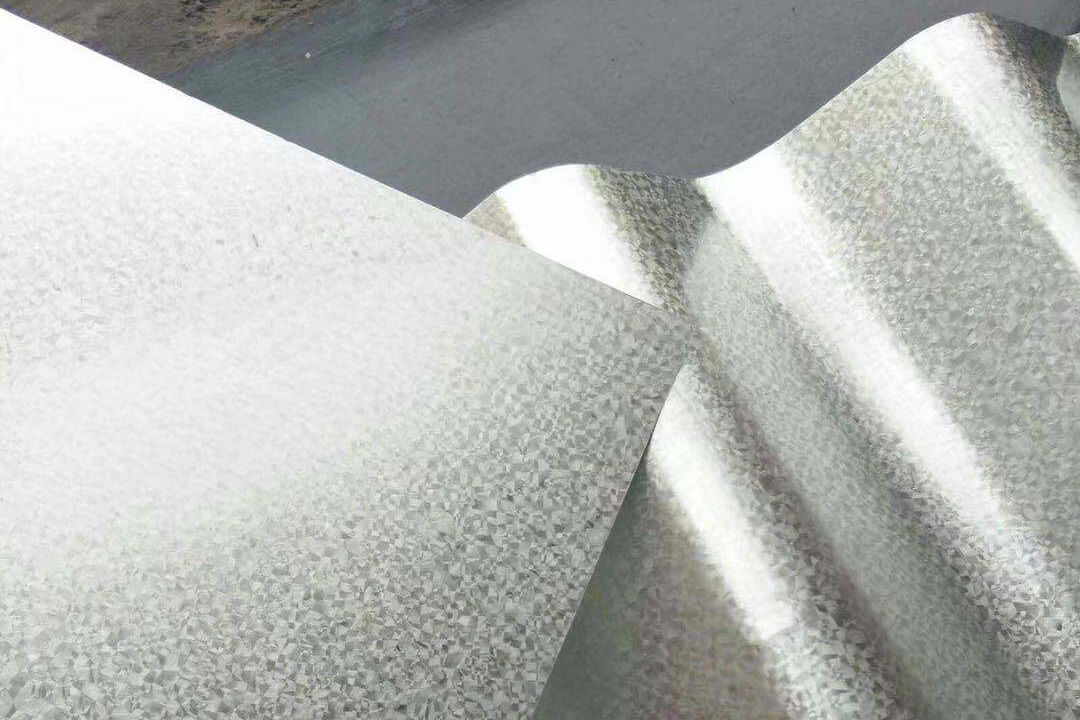
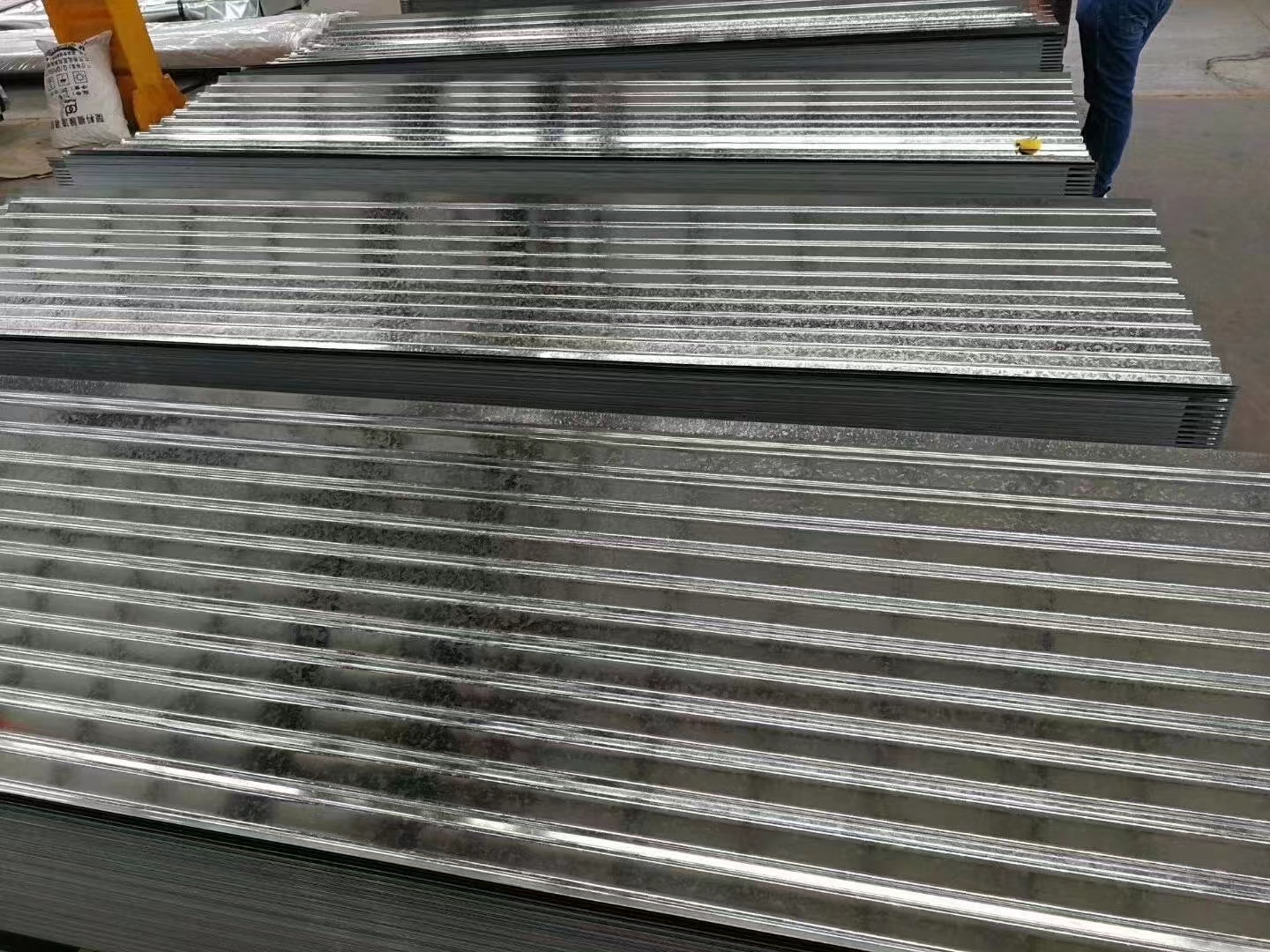
4×8 Galvanized Sheet Metal: Ideal for HVAC and More
The 4×8 galvanized sheet metals size is particularly useful in HVAC applications. It offers enough coverage for duct systems while maintaining lightweight properties for easy installation. The galvanized material is corrosion-resistant, ensuring longevity in both residential and commercial HVAC systems.
Sheet Metal Manufacturing: How It’s Made
Sheet metals manufacturing involves a series of processes to transform raw metal into usable sheets. Here’s a brief overview:
1. Rolling
Hot or cold rolling reduces the thickness of metal slabs and gives them a smooth finish.
2. Annealing
Heat treatment improves the metal’s ductility and workability.
3. Surface Treatment
Coatings like zinc (galvanization) or paint (as in PPGI steel) protect the metal from corrosion.
4. Cutting and Shaping
Laser cutting, waterjet cutting, bending, and stamping turn flat sheets into finished products.
5. Welding and Assembly
For components requiring complex structures, sheets are welded and assembled into their final forms.
Applications of Sheet Metals
Construction: Roofing, facades, wall panels (PPGI steel, aluminum).
Automotive: Body panels, exhausts (aluminum, stainless steel).
Marine: Hulls and decks (316L stainless steel, aluminum).
Appliances: Ovens, refrigerators (stainless steel sheet).
HVAC: Ducts and vents (galvanized or aluminum sheet metal).
Furniture: Decorative and functional pieces (black sheet metal).
Sustainability in Sheet Metals Production
Modern sheet metal production emphasizes sustainability through:
Recycling: Most sheet metal, especially aluminum and stainless steel, is recyclable.
Energy-efficient processes: New technologies reduce energy use during production.
Eco-friendly coatings: Safer materials are replacing hazardous chemicals in surface treatments.
Selecting the Right Sheet Metals
When selecting sheet metal for your project, consider:
Material: Aluminum for lightweight needs, stainless steel for strength, PPGI for aesthetics.
Thickness: Thicker sheets for structural integrity; thinner for flexibility.
Finish: Choose based on environmental exposure and visual appeal.
Cost: Stainless steel is more expensive than aluminum or carbon steel but offers greater longevity.
Final Thoughts
From PPGI steel and black sheet metal to stainless steel sheet metal and HVAC sheet metal, the world of sheet metal is vast and diverse. Whether you’re working on a home improvement project or managing a large industrial operation, understanding the different types of sheet metal and their applications can help you make informed decisions.
Aluminum sheet metal 4×8, alu sheet metal, and stainless steel sheets are foundational elements in many sectors, offering strength, flexibility, and durability. Paired with essential tools like the sheet metal roller, these materials can be transformed into almost any shape or structure imaginable.
As sheet metal manufacturing continues to evolve with technology, the options will only expand—delivering more sustainable, durable, and customizable solutions to meet the needs of tomorrow.
Qingdao Witop Steel group are a first-class iron and steel enterprise in China. The group mainly produce cold rolled steel, hot dipped galvanized steel, hot dipped galvalume steel, pre-painted/color coated steel, tinplate, color stone coated roof tile and other steel materials.