Introduction
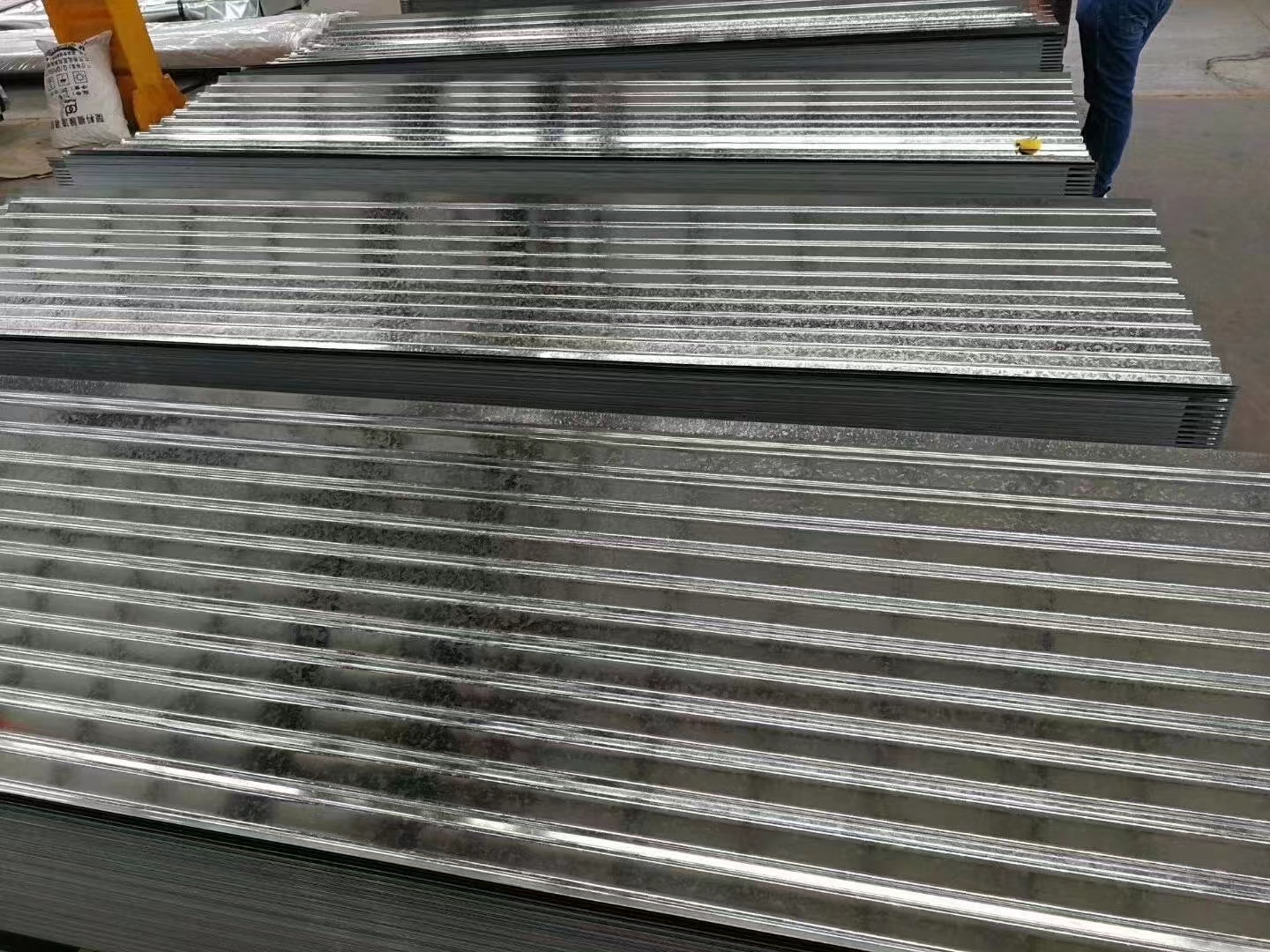
Galvanized Iron (GI) sheet metal is widely used in construction, manufacturing, and industrial applications due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and affordability.
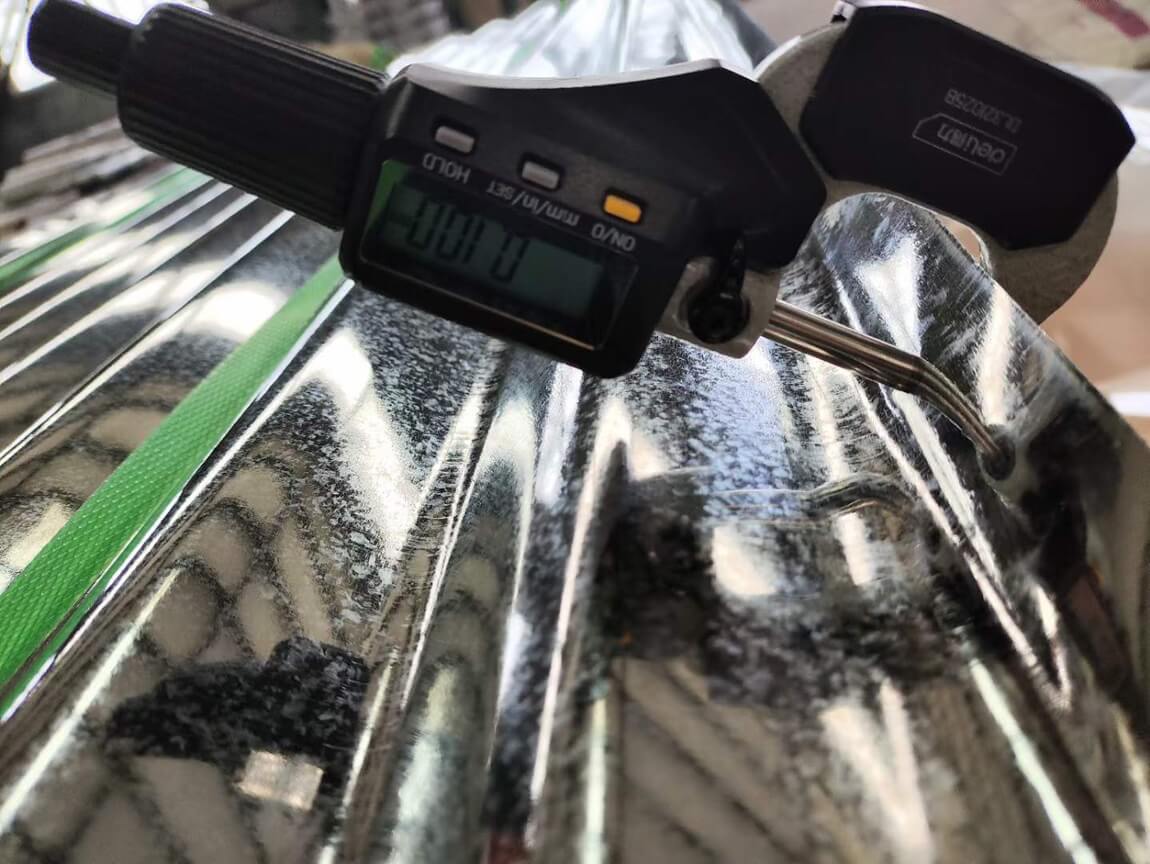
One of the most critical factors when selecting a GI sheet is its thickness, typically measured in gauge. However, gauge numbers can be confusing as they do not directly correlate to millimeter measurements.
When working with sheet metal, the term “gauge” is often used. Gauge are used to specify the thickness of a metal sheet. Gauge (Ga.) is a length measurement unit for diameters originating in North America and belongs to the Browne & Sharpe metering system. Originally used in the fields of medicine and jewellery, the larger the number, the smaller the diameter, and now it is also used to indicate the thickness.
Ga. is different from inches, there is no conversion formula. Even when the non-ferrous metal plate and the steel plate are the same Ga., the thickness is actually different.
This blog post will break down the gauge system, provide GI sheet gauge-to-mm conversions, and explore the applications of various sheet metal gauges.
What Is a Sheet Metal Gauge?
The gauge system measures the thickness of sheet metal, with a lower gauge number indicating a thicker sheet. This system originated from the wire industry but has since been widely adopted for sheet metal, including galvanized sheets.
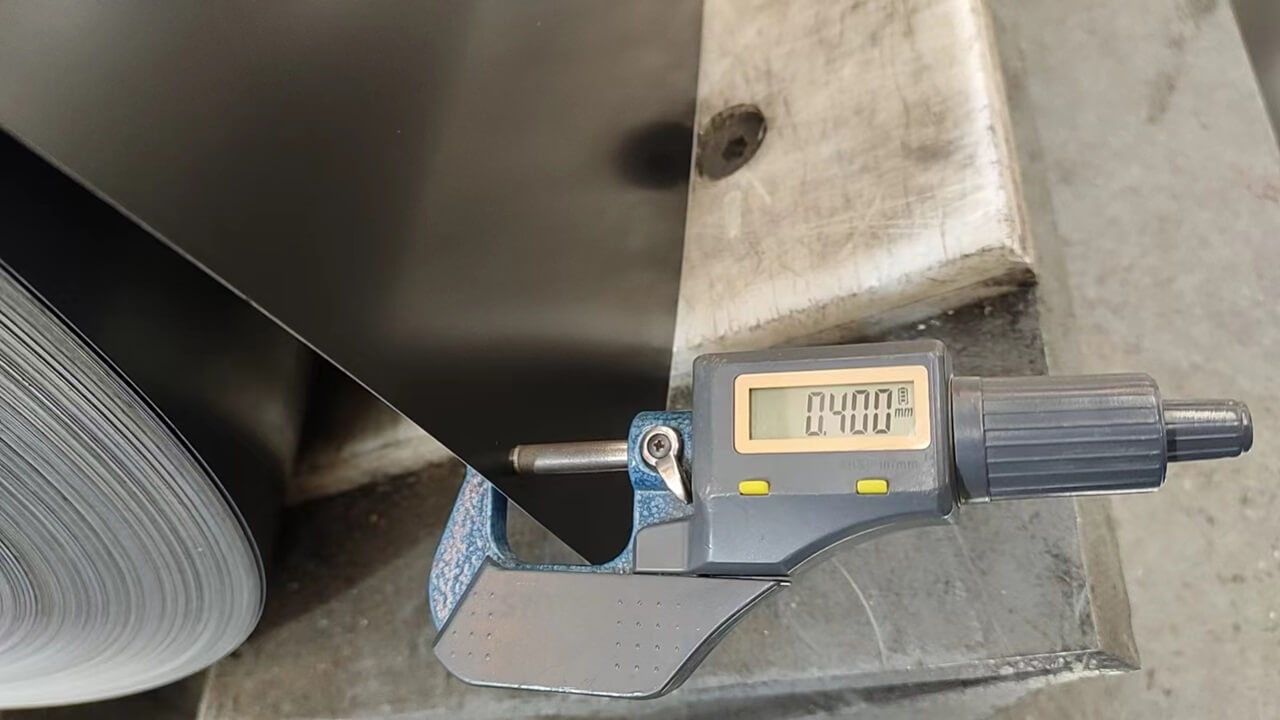

GI Sheet Gauge to mm Conversion
Below is a standard conversion chart for some common GI sheet gauges:
- 26 gauge galvanized sheet metal – 0.55 mm
- 24 gauge galvanized sheet metal – 0.63 mm
- 22 gauge galvanized sheet metal – 0.75 mm
- 20 gauge galvanized sheet metal – 0.91 mm
- 18 gauge sheet metal – 1.21 mm
- 16 gauge sheet metal – 1.52 mm
- 14 gauge sheet metal – 1.90 mm
The exact thickness may vary slightly depending on the manufacturing process and material composition.
Understanding Galvanized GI Sheet Metal Gauges
26 Gauge Sheet Metal
A 26 gauge galvanized sheet metal is relatively thin and lightweight. It is commonly used in residential roofing, ductwork, and lightweight cladding applications where minimal structural strength is required.
24 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal
A 24 gauge galvanized sheet metal is slightly thicker than 26 gauge and is preferred for stronger applications like automotive panels, siding, and medium-duty roofing sheets.
22 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal
A 22 gauge galvanized sheet metal is more robust and is used for applications requiring higher durability, such as industrial siding, HVAC ducts, and durable enclosures.
20 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal
A 20 gauge galvanized sheet metal offers even more strength and is commonly found in construction projects, metal cabinets, and automotive body panels.
18 Gauge Sheet Metal
An 18 gauge steel sheet metal is thick and highly durable. It is used for heavier applications like structural components, doors, and heavy-duty enclosures.
16 Gauge Galvanized Sheet Metal
A 16 gauge galvanized sheet metal is highly durable and is often used in structural applications such as 16 gauge corrugated metal panels, fences, and high-impact-resistant cladding.
14 Gauge Sheet Metal
A 14 gauge sheet metal is one of the thickest commonly available sheet metal options. It is used in load-bearing applications, industrial shelving, and heavy machinery enclosures.
Applications of GI Sheet Metal in Different Gauges
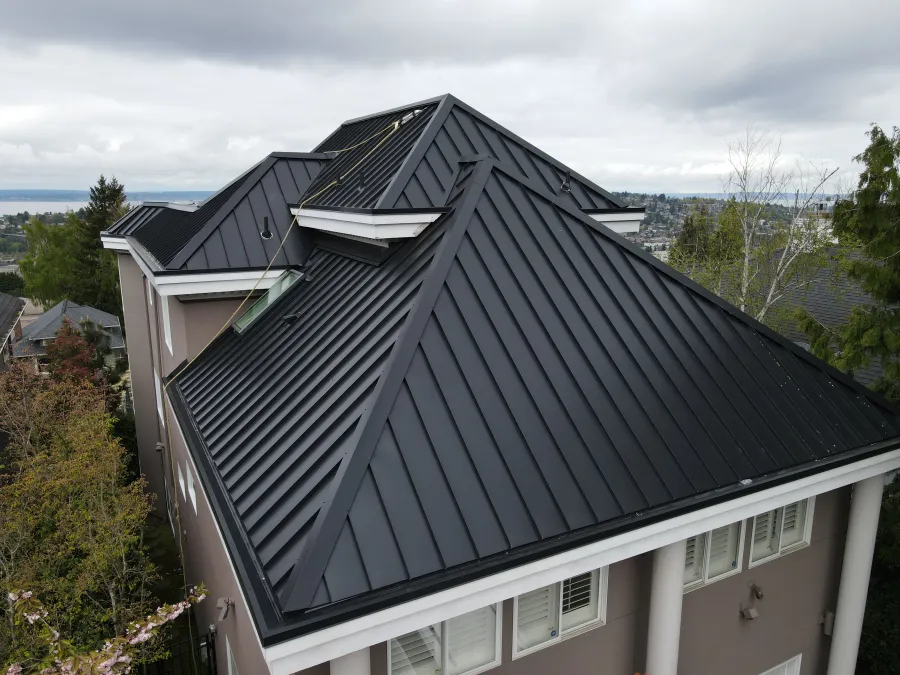
Roofing and Cladding
- Corrugated sheet metal in various gauges, including 16 gauge corrugated metal panels, is widely used for roofing, offering excellent durability and corrosion resistance.
- 26 gauge sheet metal is commonly used for residential and lightweight roofing.
Construction and Fabrication
- 20 gauge sheet metal and 22 gauge sheet metal are often used for ductwork, siding, and paneling.
- 18 gauge steel sheet metal is preferred for doors, gates, and heavy-duty structural applications.
Automotive and Industrial Applications
- 24 gauge galvanized sheet metal and 20 gauge galvanized sheet metal are used for vehicle body panels.
- 16 gauge galvanized sheet metal is used in industrial-strength applications such as machinery guards and steel enclosures.
Choosing the Right Gauge for Your Needs
Selecting the right gauge depends on the intended application. If you need a lightweight option for roofing or ductwork, 26 gauge sheet metal is ideal. For structural components, 16 gauge sheet metal or 14 gauge sheet metal would be more appropriate.
Conclusion
Understanding GI sheet gauge measurements is crucial for selecting the right material for your project. Whether you are working with 16 gauge corrugated metal panels, 22 gauge sheet metal, or 20 gauge sheet metal, knowing the thickness in millimeters ensures you get the right durability and performance. By referring to the gauge-to-mm conversion and understanding the specific applications, you can make informed decisions when choosing galvanized sheet metal.
Our company, Qingdao Witop Steel group, has GI sheets of different thickness. Our expert team helps customers decide the appropriate thickness of metal sheets as per their specific need and applications.