What To You Know the Difference Galvanized or Galvalume?
When choosing metal for construction or manufacturing, you often encounter two common options: galvanized steel and Galvalume steel. Both materials are popular for their corrosion resistance and durability, but they are not the same. Knowing their differences can help you make a better choice for your project.
1. What is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The process, known as hot-dip galvanization, involves immersing the steel in molten zinc. This creates a strong bond between the steel and the zinc coating, which acts as a barrier to prevent moisture and oxygen from reaching the metal surface.

Advantages of Galvanized Steel:
- Corrosion Resistance: Zinc provides a protective layer that prevents rust formation.
- Affordability: Galvanized steel is often less expensive than Galvalume.
- Widespread Use: Due to its durability and cost-effectiveness, galvanized steel is used in many industries, from roofing to structural frameworks.
However, galvanized steel’s zinc coating can wear off over time, especially in harsh environments, leading to corrosion.
2. What is Galvalume Steel?
Galvalume steel combines zinc and aluminum in its coating, giving it unique properties. The coating is typically composed of 55% aluminum, 43.4% zinc, and 1.6% silicon. This blend offers a combination of the corrosion resistance of aluminum with the barrier protection of zinc.
Advantages of Galvalume Steel:
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The aluminum in Galvalume increases corrosion resistance, especially in environments with moisture and chemical exposure.
- Heat Resistance: Galvalume can withstand higher temperatures without degrading, making it suitable for applications like roofing in hot climates.
- Longer Lifespan: Studies have shown that Galvalume lasts up to twice as long as galvanized steel in certain environments.
However, Galvalume can be more vulnerable to scratches due to its harder, more brittle surface.
3. Corrosion Resistance: Zinc vs. Aluminum-Zinc Coatings
Both galvanized and Galvalume steel are designed to protect the underlying steel from corrosion. However, they achieve this in different ways.
- Galvanized Steel: Zinc provides sacrificial protection. Even if the surface coating is damaged, the zinc will corrode first, protecting the steel beneath.
- Galvalume Steel: The aluminum in the Galvalume coating forms a tough barrier that is highly resistant to corrosion, but once the coating is breached, the steel can corrode faster than galvanized steel.
In coastal or industrial environments, where saltwater or chemicals can speed up corrosion, Galvalume often outperforms galvanized steel due to its superior resistance to oxidation.
4. Appearance and Aesthetics
While both materials can be painted or coated, they look different when left uncoated.
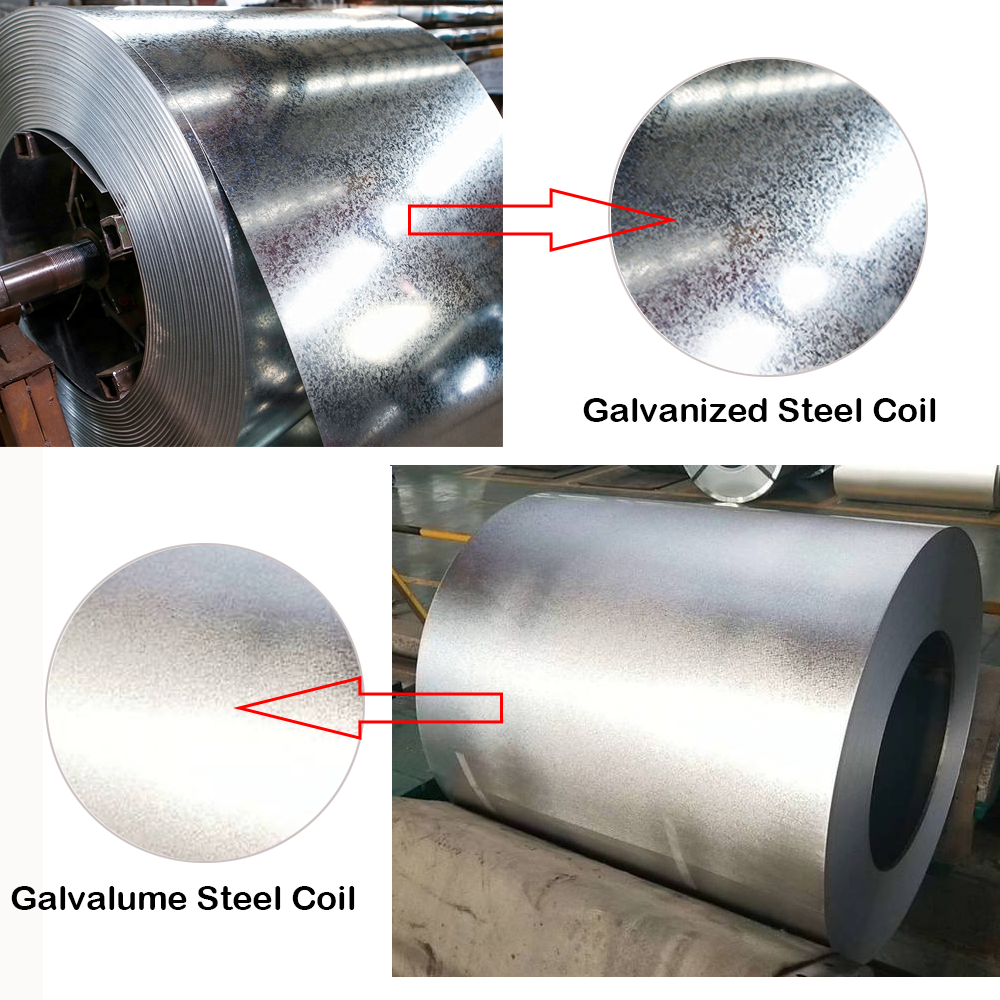
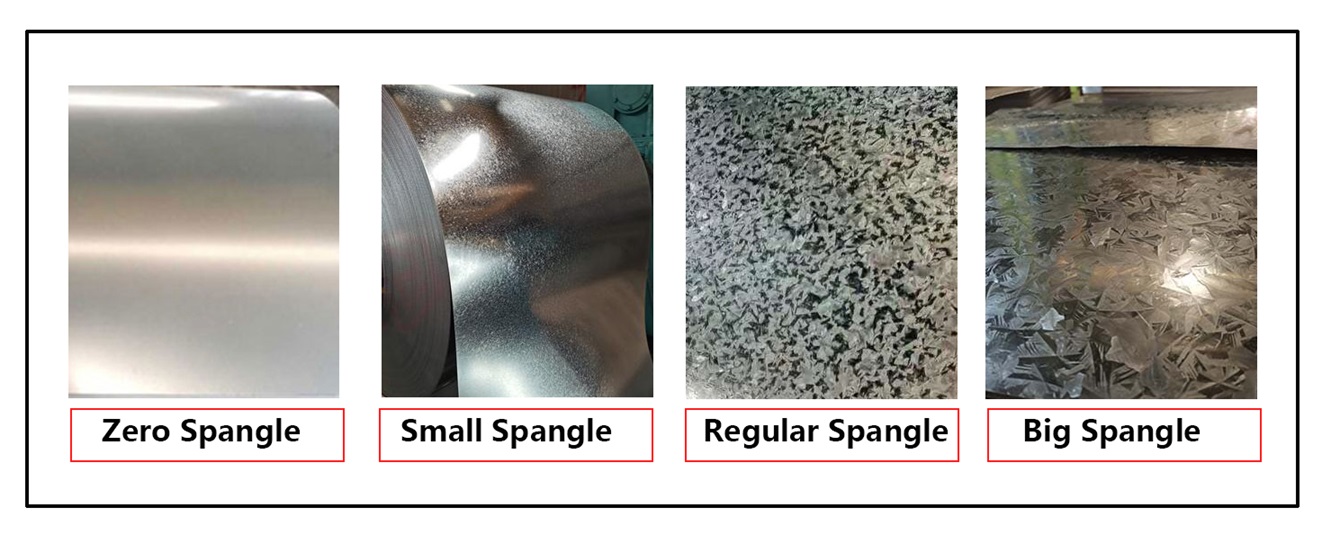
- Galvanized Steel: Has a spangled finish, which can give it a bright, shiny appearance. Over time, it will dull slightly but still maintain its protective properties.
- Galvalume Steel: Has a matte silver appearance. The aluminum gives it a smoother, more modern look, which can be preferred in architectural applications.
5. Cost Considerations
Galvalume steel is typically more expensive than galvanized steel due to the added cost of aluminum. However, the longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements of Galvalume can make it more cost-effective in the long run, especially in environments prone to corrosion.
6. Applications: Where to Use Each
- Galvanized Steel: Ideal for general construction, HVAC ducts, fences, and lower-cost roofing materials. It is especially effective in dry environments or applications where it is unlikely to get scratched.
- Galvalume Steel: Often used in more demanding applications like roofing, siding, and industrial structures where the metal is exposed to harsher conditions. Its heat resistance makes it an excellent choice for applications where temperature fluctuations are common.
7. Conclusion: Which is Right for You?
Choosing between galvanized and Galvalume steel depends on your specific needs. If you need a cost-effective option for general use, galvanized steel is a reliable choice. But if you’re working in a harsh environment or need a product that can last longer with minimal maintenance, Galvalume might be worth the extra investment.
When making your decision, consider factors such as:
- Environmental conditions (humidity, coastal exposure) Consider the specific environmental conditions where the steel will be used. If the environment is corrosive, such as near the coast, Galvalume may be a better choice.
- Budget If cost is a primary concern and the environment is not highly corrosive, galvanized steel might be a more economical option.
- Expected lifespan: The aesthetic preferences for the project may influence the choice between the two, as the appearance of the coatings can differ.